Island Reversal Chart Pattern: Psychology, Trading Strategies, and Risk Management
1. Introduction to the Island Reversal
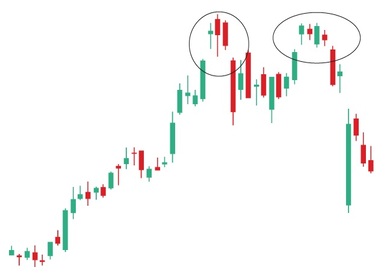
The Island Reversal chart pattern is a rare but powerful reversal signal in technical analysis.
It forms when a cluster of price bars becomes isolated by gaps on both sides, creating the appearance of an “island” on the chart.
This pattern indicates a sharp shift in market sentiment, often leading to a strong reversal in price direction.
Traders view island reversals as warnings that the prevailing trend is losing momentum and a new trend is about to begin.
2. Anatomy of the Island Reversal
- Gap Before Island: A gap in the direction of the prevailing trend isolates the start of the island.
- Island Formation: A group of candlesticks trades within a narrow range, disconnected from prior price action.
- Gap After Island: A gap in the opposite direction isolates the end of the island, confirming reversal.
- Volume Behavior: Volume often spikes during gaps, reflecting strong sentiment shifts.
3. Market Psychology Behind Island Reversals
- Initial Gap: Traders chase momentum, driving price sharply in one direction.
- Island Phase: Market consolidates, but sentiment begins to weaken.
- Final Gap: A sudden shift in psychology occurs — buyers turn into sellers or vice versa.
- Reversal: The market abandons the prior trend, leading to sharp moves in the opposite direction.
This reflects investor psychology:
- Herd behavior drives initial gap.
- Confusion and indecision dominate during the island.
- Panic or euphoria triggers the final gap.
- Smart money exploits sentiment extremes to reverse positions.
4. Types of Island Reversals
| Type | Direction | Typical Context | Psychology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bullish Island Reversal | Downtrend → Uptrend | Gap down, consolidation, gap up | Sellers exhausted, buyers regain control |
| Bearish Island Reversal | Uptrend → Downtrend | Gap up, consolidation, gap down | Buyers exhausted, sellers regain control |
5. How to Trade the Island Reversal
Entry Strategies
- Breakout Entry: Enter in the direction of the final gap after confirmation.
- Retest Entry: Wait for price to retest gap zone before entering.
- Aggressive Entry: Trade immediately after the final gap with tight stop-loss.
Stop-Loss Placement
- Below the gap for bullish reversals.
- Above the gap for bearish reversals.
Profit Targets
- Measure height of island range.
- Project move equal to that height after breakout.
- Use prior support/resistance zones for targets.
6. Common Mistakes Traders Make
- Misidentifying ordinary gaps as island reversals.
- Entering trades without confirmation.
- Ignoring volume signals.
- Over-leveraging positions.
7. Advanced Trading Strategies
- Indicator Confirmation: Use RSI divergence, MACD crossovers, or moving averages.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Confirm island reversal on higher timeframes.
- Volume Profile Integration: Analyze volume distribution during gaps.
- Candlestick Patterns: Look for engulfing or doji candles within the island.
8. Island Reversal vs. Other Gap Patterns
| Feature | Island Reversal | Breakaway Gap | Exhaustion Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Gaps on both sides | Gap at start of trend | Gap at end of trend |
| Psychology | Sentiment shift | Conviction shift | Weakening momentum |
| Reliability | High | High | Moderate |
9. Risk Management in Island Reversal Trading
- Always use stop-loss orders.
- Avoid trading without gap confirmation.
- Manage position size carefully.
- Diversify trades to reduce exposure.
10. Case Studies: Island Reversals in Different Markets
- Stocks: Common after earnings surprises or corporate announcements.
- Forex: Appears during macroeconomic shocks or geopolitical events.
- Crypto: Frequently seen during speculative rallies and crashes.
11. Conclusion
The Island Reversal chart pattern is a rare but highly reliable reversal signal. By understanding its psychology and applying disciplined trading strategies, traders can anticipate sharp market turning points. Success requires patience, confirmation, and strict risk management.