Mastering Trend Lines, Trading Psychology, and Proven Strategies: A Complete Guide for Traders
Introduction: Why Trend Lines and Psychology Define Trading Success
Trading is not just about numbers on a chart—it’s a blend of technical analysis, psychological discipline, and strategic execution. Many traders fail not because they lack knowledge of indicators, but because they misunderstand trend lines, ignore psychology, or lack a clear strategy. This guide explores these three pillars in depth, offering actionable insights for beginners and professionals alike.
Part 1: Understanding Trend Lines in Trading
What is a Trend Line?
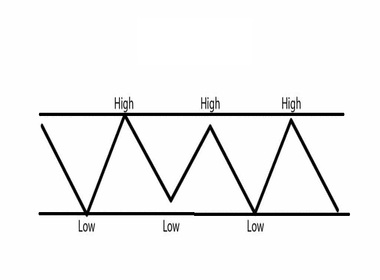
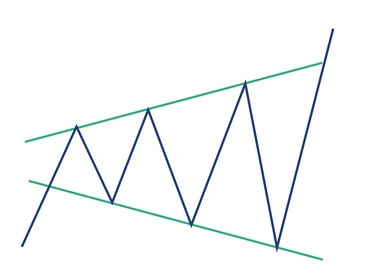
A trend line is a straight line drawn on a chart that connects two or more price points, helping traders visualize the direction of the market. It acts as a guide to identify support, resistance, and overall momentum.
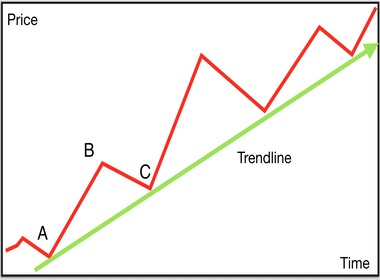
- Uptrend line: Drawn by connecting higher lows, showing bullish momentum.
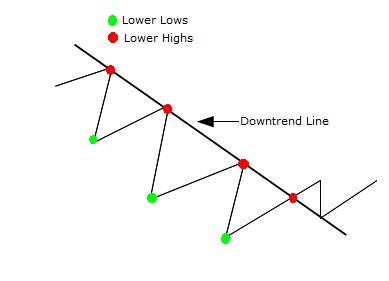
- Downtrend line: Drawn by connecting lower highs, showing bearish momentum.
- Sideways trend line: Indicates consolidation or range-bound markets.
Why Trend Lines Matter
- Provide clarity in chaotic price movements.
- Help identify entry and exit points.
- Offer confirmation when combined with other indicators (RSI, MACD, moving averages).
How to Draw Accurate Trend Lines
- Use major swing highs/lows.
- Avoid forcing lines to fit your bias.
- Confirm with multiple touches (at least 2–3 points).
- Adjust trend lines as new data emerges.
Common Mistakes Traders Make
- Drawing lines on minor fluctuations.
- Ignoring timeframe relevance.
- Over-relying on trend lines without confirmation.
Part 2: The Psychology of Trading
What is Trading Psychology?
Trading psychology refers to the mental and emotional state that influences decision-making in financial markets. It includes discipline, patience, confidence, and emotional control.
Key Psychological Biases in Trading
- Fear of Loss: Closing trades too early.
- Greed: Over-leveraging or chasing profits.
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking data that supports your belief.
- Overconfidence: Ignoring risk management after a winning streak.
Building a Strong Trading Mindset
- Discipline: Stick to your plan, avoid impulsive trades.
- Patience: Wait for high-probability setups.
- Resilience: Accept losses as part of the process.
- Adaptability: Adjust strategies when markets change.
Techniques to Improve Trading Psychology
- Journaling trades to track emotions.
- Practicing mindfulness or meditation.
- Using smaller position sizes to reduce stress.
- Setting realistic goals.
Part 3: Trading Strategies That Work
Trend-Following Strategy
- Identify the dominant trend using trend lines.
- Enter trades in the direction of the trend.
- Use stop-loss below support (for long) or above resistance (for short).
Breakout Strategy
- Watch for price breaking above resistance or below support.
- Confirm with volume.
- Enter after breakout retest for higher accuracy.
Swing Trading Strategy
- Focus on medium-term moves.
- Combine trend lines with oscillators (RSI, Stochastic).
- Aim for risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
Scalping Strategy
- Trade small price movements on lower timeframes.
- Requires discipline and quick decision-making.
- Use tight stop-losses.
Psychological Strategy Integration
- Match strategy with your personality.
- If you’re patient → swing trading.
- If you’re fast-paced → scalping.
- If you prefer long-term → trend-following.
Part 4: Combining Trend Lines, Psychology, and Strategy
The Three Pillars of Trading Success
- Trend Lines → Technical clarity.
- Psychology → Emotional stability.
- Strategy → Practical execution.
Example Workflow
- Identify trend with lines.
- Confirm with indicators.
- Choose strategy (trend-following, breakout).
- Apply psychological discipline (no revenge trading).
- Execute with risk management.
Part 5: Advanced Insights
Multi-Timeframe Analysis
- Use higher timeframe trend lines for context.
- Trade on lower timeframe for precision.
Risk Management
- Never risk more than 1–2% per trade.
- Use stop-loss and take-profit levels.
- Diversify across assets.
Case Study: Trend Line + Psychology in Action
Imagine a trader sees an uptrend line forming. Instead of rushing in, they wait for confirmation. Their patience prevents a false breakout loss. This is where psychology saves capital.
Conclusion: The Path to Trading Mastery
Trading success is not about predicting the market perfectly—it’s about combining trend line analysis, psychological discipline, and strategic execution. Master these three, and you’ll transform chaos into clarity.